Lazy Tongue: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options
By Rajini D
Last Updated: May 9, 2024
Have you ever heard the term ‘lazy tongue’ and wondered what it means? You’re not alone”. Lazy tongue isn’t a clinical term, but it’s often used to describe various speech symptoms and potential diagnoses that can affect both children and adults. Whether it’s slurred speech, mispronounced sounds, or difficulty moving the tongue, a ‘lazy tongue’ could be a sign of an underlying condition that needs attention.
Understanding Lazy Tongue: What Is It Exactly?

Defining Lazy Tongue:
Lazy tongue, also known as tongue-tie or ankyloglossia, refers to a condition where the frenulum—the thin strip of tissue under the tongue—is too short, thick, or tight. This restricts tongue movement, leading to speech difficulties and other challenges.
Related terms often used include sluggish tongue, tongue weakness, and speech difficulty. A lazy tongue is sometimes used more broadly to describe speech issues caused by other conditions like dysarthria or a lisp.
Also read: What is Lisp: How Speech Therapy can help you deal with it
Who Is Affected:
- Newborns:
Lazy tongue primarily affects newborns, with an estimated prevalence of 4-11%. It’s more common in boys and often runs in families. Parents might notice difficulty with breastfeeding, such as trouble latching or prolonged feeding times. - Children:
Children with Down syndrome and other genetic conditions are more prone to having a tongue-tie. Symptoms in children may include speech issues, difficulty eating solid foods, and challenges with oral hygiene. - Adults:
While less documented in adults, the lazy tongue can persist if left untreated. Symptoms might include slurred speech, difficulty articulating certain sounds, and problems with oral health. For instance, adults with ankyloglossia might struggle to brush their teeth properly or maintain dental hygiene.
Know more: Dealing with Lazy Tongue: Tips and Tricks
Why Is It Important to Understand Lazy Tongue?
Understanding the lazy tongue is crucial for early intervention and treatment. If you or your child are experiencing symptoms, a speech therapy evaluation can identify the issue and provide practical solutions.
Causes and Related Speech Disorders
Dysarthria:
Dysarthria is a motor-speech disorder that leads to slurred or mumbled speech due to weak tongue muscles. It’s often a result of damage to parts of the brain that control muscle movements, affecting the clarity and pace of speech.
Symptoms of Dysarthria Include:
- Unclear, slurred, or mumbled speech
- Drooling due to difficulty controlling saliva
- Trouble chewing and swallowing
- Difficulty controlling speech volume and pace
- Fatigue when speaking for extended periods
Wellness Hub’s Insight:
If you or your loved one struggles with dysarthria, our Speech Therapy for Adults can help you strengthen speech muscles and improve articulation.
Lisp:
A lisp is a speech disorder where incorrect tongue placement leads to mispronunciation, often affecting “s” and “z” sounds. People with a lisp might push their tongue against their teeth or protrude it between their teeth, causing a distorted sound.
Types of Lisps Include:
- Palatal Lisp:
- Tongue touches the roof of the mouth (soft palate).
- Difficulty pronouncing “s” and “z” sounds.
- Lateral Lisp:
- Air escapes from one or both sides of the mouth.
- Words sound “wet” or “spitty.”
- Dentalized Lisp:
- Tongue pushes against the front teeth, causing a muffled sound.
- Interdental Lisp (Frontal Lisp):
- Tongue protrudes between the front teeth, often producing a “th” sound instead of “s” or “z.”
Know more: 6 Varieties of Lisps and How to Overcome Them
Tongue-Tie (Ankyloglossia):
Tongue-tie, or ankyloglossia, occurs when the frenulum (thin strip of tissue under the tongue) is too short, thick, or tight, restricting tongue movement.
Symptoms of Tongue-Tie Include:
- Difficulty lifting the tongue to the upper teeth
- Trouble moving the tongue side-to-side
- Heart-shaped tongue when sticking it out
- Problems breastfeeding (in infants)
- Difficulty chewing solid foods
- Pocketing food in the cheeks or choking
Symptoms of Lazy Tongue
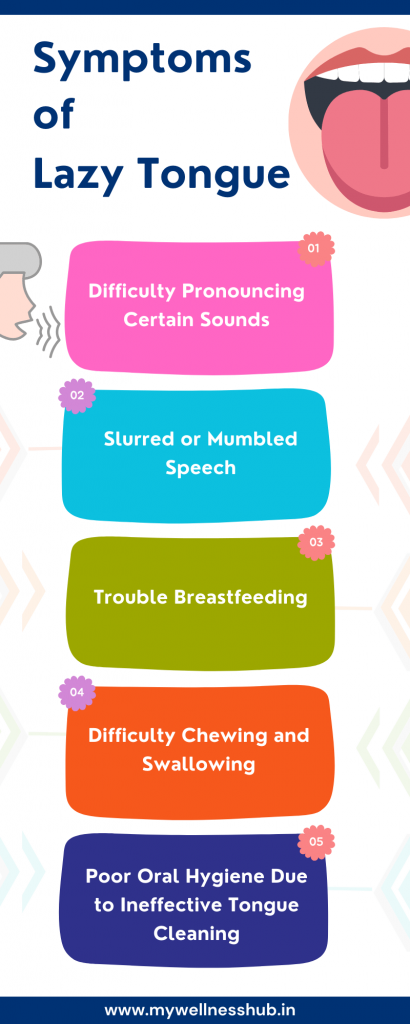
Difficulty Pronouncing Certain Sounds (e.g., “s,” “z”)
If you’ve noticed someone struggling to pronounce specific sounds like “s” or “z,” this could be a sign of lazy tongue. For instance, people with a lisp often substitute these sounds with “th,” making “sun” sound like “thun.” Incorrect tongue placement or restricted tongue movement due to tongue-tie or dysarthria can make it challenging to articulate these sounds clearly.
Slurred or Mumbled Speech
Lazy tongue can result in slurred or mumbled speech, often described as unclear or garbled. Dysarthria, a motor-speech disorder, weakens the tongue muscles, making it difficult to control the pace and clarity of speech. Adults with slurred speech may find it embarrassing or frustrating to communicate, impacting their confidence and social interactions.
Trouble Breastfeeding (in Infants)
Infants with tongue-tie may have trouble breastfeeding due to difficulty latching onto the breast or maintaining proper suction. Signs include prolonged feeding times, fussiness during feeding, or a clicking sound while sucking. If left untreated, this can lead to poor weight gain or dehydration.
Difficulty Chewing and Swallowing (Food Pocketing in Cheeks)
Chewing and swallowing require precise tongue movements. When the tongue can’t move freely due to tongue-tie or weak muscles, food may pocket in the cheeks or lead to gagging or choking. This makes mealtimes difficult, particularly for children transitioning to solid foods.
Poor Oral Hygiene Due to Ineffective Tongue Cleaning
A lazy tongue can hinder effective tongue cleaning, leading to poor oral hygiene. When food debris isn’t cleared from the tongue, it can contribute to bad breath and increase the risk of dental problems like cavities and gum disease.
Diagnosing Lazy Tongue
Importance of Professional Evaluation:
If you suspect lazy tongue, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper assessment. A Speech-Language Pathologist plays a crucial role in diagnosing speech disorders like dysarthria, lisps, and tongue-tie. They can also refer you to a doctor or dentist if surgical intervention is needed.
Here’s what a thorough evaluation might include:
Key Diagnosis Criteria:
- Frenulum Assessment:
- An SLP or dentist will examine the frenulum under the tongue to identify if it’s too short, thick, or tight (a condition known as tongue-tie).
- They’ll observe how the tongue moves during speech and oral functions, such as eating and swallowing.
- Speech Evaluation for Dysarthria or Lisp Patterns:
- The SLP will listen to your speech and identify any slurred, mumbled, or unclear sounds.
- They will check for lisp patterns like interdental or lateral lisps by observing tongue placement and articulation.
- Assessment of Tongue Movement Limitations:
- You’ll be asked to move your tongue in different directions (up, down, and side-to-side) and stick it out to assess mobility.
- Limited tongue movement, especially difficulty lifting it to the upper teeth, can indicate tongue-tie.
Read more: How Long Will My Child Need Speech Therapy?
Treatment Options for Lazy Tongue
Frenotomy:
A frenotomy is a simple surgical procedure that involves cutting the frenulum to release the tongue and allow greater mobility. It is especially effective for infants struggling with breastfeeding issues. The procedure is quick and typically performed under local anesthesia in a doctor’s office.
Benefits of Frenotomy:
- Immediate improvement in breastfeeding ability for infants.
- Enhanced tongue mobility for better articulation and speech clarity.
- Quick recovery time, often just a few days.
Frenuloplasty:
Frenuloplasty is a more extensive procedure that involves making a small incision in the frenulum and then reattaching the tongue to the floor of the mouth with sutures. It’s recommended for individuals with severe tongue-ties that can’t be adequately treated with frenotomy.
Benefits of Frenuloplasty:
- Allows for greater tongue mobility in severe cases.
- It can improve speech and swallowing difficulties.
- Typically done under general anesthesia, with a recovery period of about 1-2 weeks.
Speech Therapy:
Speech therapy is essential for treating lazy tongue, whether caused by dysarthria, lisps, or tongue-tie. A Speech-Language Pathologist (SLP) will create a personalized treatment plan to address specific speech challenges.
Dysarthria Treatment:
- Focuses on strengthening the speech muscles.
- Helps improve articulation and speech clarity.
- Includes practice in pacing and communication.
Lisp Therapy:
- Correct tongue placement for accurate pronunciation of “s” and “z” sounds.
- Helps differentiate between correct and incorrect sounds.
- Gradually, it increases the complexity of structured sentences and spontaneous speech.
Post-Frenotomy Therapy:
- Ensures proper tongue movement after surgery.
- Includes exercises to improve articulation and speech patterns.
- Supports gradual improvement in speech clarity.
Myofunctional Therapy:
Myofunctional therapy focuses on retraining the oral muscles to improve tongue control and strengthen speech clarity. It’s particularly beneficial for individuals with swallowing difficulties or weak tongue muscles.
Benefits of Myofunctional Therapy:
- Helps with chewing and swallowing issues.
- Improves tongue control for clearer speech.
- It can reduce food pocketing in the cheeks.
Read more: Oral Motor Exercises: Tongue Exercises for Confident Speech
Overview of Lazy Tongue Treatment Options
| Treatment | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Frenotomy | A simple surgical procedure where the frenulum is cut, allowing greater tongue movement. | – Quick and effective, especially for infants with breastfeeding issues. – Immediate improvement in tongue mobility and feeding ability. – Minimal recovery time. |
| Frenuloplasty | An extensive surgical procedure that involves cutting the frenulum and using sutures. | Personalized therapy plans were created by a Speech-Language Pathologist (SLP) to address dysarthria, lisps, and post-surgery improvements. |
| Speech Therapy | Personalized therapy plans created by a Speech-Language Pathologist (SLP) to address dysarthria, lisps, and post-surgery improvements. | – Improves articulation and pronunciation. – Strengthens speech muscles for better tongue control. – Helps with pacing, articulation, and pronunciation. |
| Myofunctional Therapy | Retrains the oral muscles through exercises to improve tongue control and function. | – Helps with speech difficulties and swallowing problems. – Reduces food pocketing and enhances oral hygiene. – Improves overall tongue strength and flexibility. |
Practical Tips for Managing Lazy Tongue
Exercises to Improve Tongue Movement:
- Tongue Stretching Exercises:
- Up-Down Stretch: Stick your tongue out as far as possible, then move it up to touch your nose and down to touch your chin. Repeat 10 times.
- Side-to-Side Stretch: Stick your tongue out and move it from one corner of your mouth to the other. Repeat 10 times.
- Sound Practice with Tongue Placement:
- Practice sounds like “s” and “z” by placing your tongue behind your upper teeth.
- Use a mirror to monitor tongue placement and adjust as needed.

Speech Therapy Exercises:
- Personalized Program:
- Work with a speech therapist to tailor exercises specific to your speech challenges.
- Wellness Hub Insight: At Wellness Hub, our Online Speech Therapy sessions provide personalized plans for each individual.
- Daily Practice:
- Dedicate 10-15 minutes daily to articulation and pronunciation drills.
- Practice tongue twisters to enhance speech clarity.
Monitor Oral Hygiene:
- Regular Tongue Cleaning Techniques:
- Use a tongue scraper or soft toothbrush to clean your tongue daily.
- Incorporate mouthwash into your routine to reduce bacteria buildup.
- Watch Out for Food Pocketing:
- After meals, ensure no food is pocketed in the cheeks or stuck on the tongue.
- Rinse your mouth with water after eating.
Conclusion
A lazy tongue affects speech and oral health but is manageable with the right treatment. If you or someone you know has trouble with speech clarity or struggles with eating and breastfeeding, help is available. Treatments like frenotomy, frenuloplasty, and speech therapy can significantly improve speech and reduce difficulties. At Wellness Hub, our speech therapy experts provide comprehensive assessments and personalized treatment plans to help individuals of all ages achieve clearer communication.
If you suspect a lazy tongue, don’t hesitate to seek professional advice. Wellness Hub’s online speech therapy services cater to both children and adults. Our team is dedicated to helping you or your loved ones speak with confidence. Visit us online at Wellness Hub to learn more about how we can assist you in overcoming speech challenges. Take the first step today towards better communication by reaching out for professional help.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What does “lazy tongue” mean?
Lazy tongue, also known as tongue-tie or ankyloglossia, refers to a condition where the frenulum under the tongue is too short or thick, limiting tongue movement. This can lead to speech difficulties, lisps, and challenges with breastfeeding or eating.
2. How do I know if I have a lazy tongue?
Common symptoms include difficulty pronouncing certain sounds like “s” and “z,” slurred or mumbled speech, and trouble moving the tongue up or side to side. If you suspect you have a lazy tongue, consult a speech therapist for an evaluation.
3. Is lazy tongue a speech disorder?
Lazy tongue itself isn’t a clinical term but often points to underlying speech disorders like dysarthria, lisps, or tongue-tie. Proper diagnosis is crucial to finding the right treatment and improving speech clarity.
4. How can I fix a lazy tongue?
Treatments include frenotomy, frenuloplasty, speech therapy, and myofunctional therapy. Working with a speech therapist can help tailor exercises and practices that improve tongue movement and speech clarity.
5. How does speech therapy help with a lazy tongue?
Speech therapy strengthens tongue muscles, corrects tongue placement for accurate pronunciation, and improves articulation. Personalized therapy plans can help individuals speak clearly and confidently.
6. What are the causes of lazy tongue in adults and kids?
In kids, the lazy tongue is often due to tongue-tie, lisps, or genetic conditions like Down syndrome. In adults, it may be caused by dysarthria, muscle weakness, or tongue-tie that wasn’t treated in childhood.
7. What are some exercises to improve tongue movement?
Tongue stretching exercises like moving the tongue up-down and side-to-side, combined with pronunciation practice for “s” and “z” sounds, can enhance tongue flexibility and speech clarity.
8. How can Wellness Hub help with lazy tongue treatment?
Wellness Hub offers personalized speech therapy services for kids and adults, providing tailored treatment plans that address lazy tongue challenges. Our online sessions make therapy accessible and convenient.
9. What are the early signs of lazy tongue in children?
Early signs include difficulty breastfeeding, slurred or unclear speech, and trouble chewing solid foods. Children may also struggle to pronounce specific sounds like “s” and “z,” and their tongue may appear notched when sticking it out.
10. What should I do if I suspect my child has a lazy tongue?
If you suspect your child has a lazy tongue, consult a speech-language pathologist (SLP) or healthcare professional. An SLP can diagnose the condition and recommend suitable treatments like speech therapy or frenotomy if necessary.
About the Author:
Rajini Darugupally
M.Sc., Speech-Language Pathologist (9+ years of experience)
Rajini is a passionate and dedicated Speech-Language Pathologist with over 9+ years of experience, specializing in both developmental speech and language disorders in children and rehabilitation in adults. Driven by a desire to empower each individual to find their voice, Rajini brings a wealth of experience and a warm, genuine approach to therapy.
Currently, at Wellness Hub, she thrives in a team environment that values innovation, compassion, and achieving results for their clients.
Connect with Rajini to learn more about how she can help you or your loved one find their voice.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message








