The Role of Eye Contact in Your Child’s Speech and Language Development
By Rajini D
Last Updated: December 22, 2023
Eye contact isn’t just a social nicety; it’s a cornerstone of effective learning, particularly crucial for children with language delays. Many of these children show remarkable aptitude in handling nonverbal cues. By nurturing visual performance skills, we unlock a doorway not only to improved visual attention but also to a spectrum of essential developmental skills. This article delves into the transformative power of these skills and offers practical strategies to foster them.
Book Free Speech and Language Consultation.
The Importance of Visual Performance Skills
Visual performance skills extend beyond mere eye contact. They encompass a child’s ability to track moving objects, recognize patterns, and interpret visual information. These skills are foundational for reading, writing, and social interaction. For children with language delays, enhancing visual skills can lead to significant improvements in overall communication abilities.
A Guide to Speech and Language Milestones from Birth to 7 Years.
Activities to Improve Eye Contact and Visual Skills
To facilitate the development of eye contact and visual skills, a variety of engaging activities can be employed. These activities are designed to be enjoyable and interactive, helping children to naturally improve their visual performance skills. Below is a table listing several activities along with their specific objectives, providing a practical guide for parents and educators to follow.
| S.No | Task name | Task objective |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bubbles | Bubbles encourage the child to look at you. When the child looks at you, blow some more bubbles. |
| 2. | Peek-a-boo | Play peek-a- boo with your child. Use different objects to hide your face e.g. hands, cushion, scarf. |
| 3. | Stencil | Cut out a rectangular stencil, place it near to your eyes and then on child’s eyes, do it several times. |
| 4. | Sing Rhymes | Sign Rhymes with actions |
| 5. | Torch light and Candle | In the dark room use the torch light on the wall. Then gradually move the light (move in 180 degrees). Child learns to follow the light. |
| 6. | Stencils with torch | Use torch light with stencil of torch to make it more interesting to the child. |
| 7. | Disco lights or running lights | Use moving lights in the dark room, it promotes eye tracking. |
| 8. | Lava lamp and sand timer | Keep at the level of the face, let the child watch it |
| 9. | Stickers | Put stickers on our face. Gradually put them closer to your eyes |
| 10. | Face masks, eye masks, and funny Goggles | Put face masks and eye masks by sitting in front of the child. |
| 11. | Balloons | Child looks at us when we blow a balloon, inflate the balloon and let it go off. Then try and catch it. |
| 12. | Moving and sound making toys | Give the key and leave in front of the child. Children watch these moving objects |
| 13. | Puppets | Use hand puppets at the face level and make exaggerated and funny sounds. Children enjoy it. |
| 14. | Face painting | While painting your child’s face, we will create natural proximity and be looking into each other’s faces. |
| 15. | Silliness | Make funny faces or use silly getups such as clown noses. |
| 16. | Mirror | Make funny faces before the mirrors (open the mouth widely, protrude lips, make like fish etc) |
| 17. | Push them on a swing | Stand in front of them while pushing them on a swing. This encourages eye contact and is great vestibular sensory input. |
| 18. | Wearing stone necklace and dark lipstick | Bright necklace and lip color would evoke child’s eye contact and attention towards it. |
All these activities are not only fun but also instrumental in enhancing visual attention and interpretative skills. Consistent engagement in these tasks can lead to notable improvements in a child’s ability to focus, understand, and interact with their surroundings.
Book Online Speech therapy now.
Level 2- Visual Performance (Matching Activities)
As children progress in developing their visual skills, matching activities can be introduced. These tasks are crucial for enhancing pattern recognition, spatial awareness, and memory. The following table outlines various matching activities, each with a distinct objective and material model. It helps to further advance their visual performance abilities.
| S.no | Task name | Task objective | Model of material |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Puzzle with a single piece type of inset | The child has to put single uniquely-shaped puzzle pieces into a frame board |  |
| 2. | Form box | When provided a form box or a shape sorter and its pieces, the child has to put the pieces into the corresponding holes in the form box. |  |
| 3. | Object to object matching | The child has to match the object to an identical object presented in an array of three |  |
| 4. | Object to picture matching | The child has to match object to corresponding picture in an array |  |
| 5. | Picture to picture | The child has to match picture to an identical picture presented in an array of three |  |
| 6. | Picture to object | The child has to match picture of an object to the corresponding object in an array of three |  |
| 7. | Fluent matching | When given a group of ten pictures of items, the child has to match picture to an identical picture in an array of ten in a quick succession |  |
Matching activities not only reinforce visual discrimination skills but also lay a strong foundation for academic skills like reading and mathematics. Besides, regular practice of these activities can significantly boost a child’s cognitive and visual processing abilities.
Navigating Online Speech Therapy for Non-Verbal Children: A Guide for Parents and Educators.
Level 3- Visual Performance (Sorting)
Sorting activities represent the next stage in visual performance skill development. These exercises are designed to sharpen a child’s ability to categorize and organize visual information, a key skill in both academic and daily life contexts. The table below provides a range of sorting tasks, each tailored to enhance specific aspects of visual cognition.
| S.no | Task name | Task objective | Model of material |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sort non identical items | The child has to sort non identical items into appropriate groups when sample of those items are displayed in an array (dogs, trees, people) |  |
| 2. | Block designs on the picture card | When given a block design card, child has to place the blocks in an appropriate location on the design card |  |
| 3. | Puzzles with multiple connecting pieces in an inset type frame | The has to complete puzzles with uniquely-shaped connecting pieces which fit into an irregularly shaped inset frame |  |
| 4. | Puzzles with the squared edged border frame | The child has to complete puzzles with connecting pieces which fits into a square edged frame |  |
| 5. | Block designs from picture | When given a block design card, the child has to place blocks to make the design shown on the card |  |
| 6. | Sequence pattern to match a visual model | When presented with a visual sequence pattern consisting of items (e.g., colored blocks), the child must arrange successive items to match the pattern. | 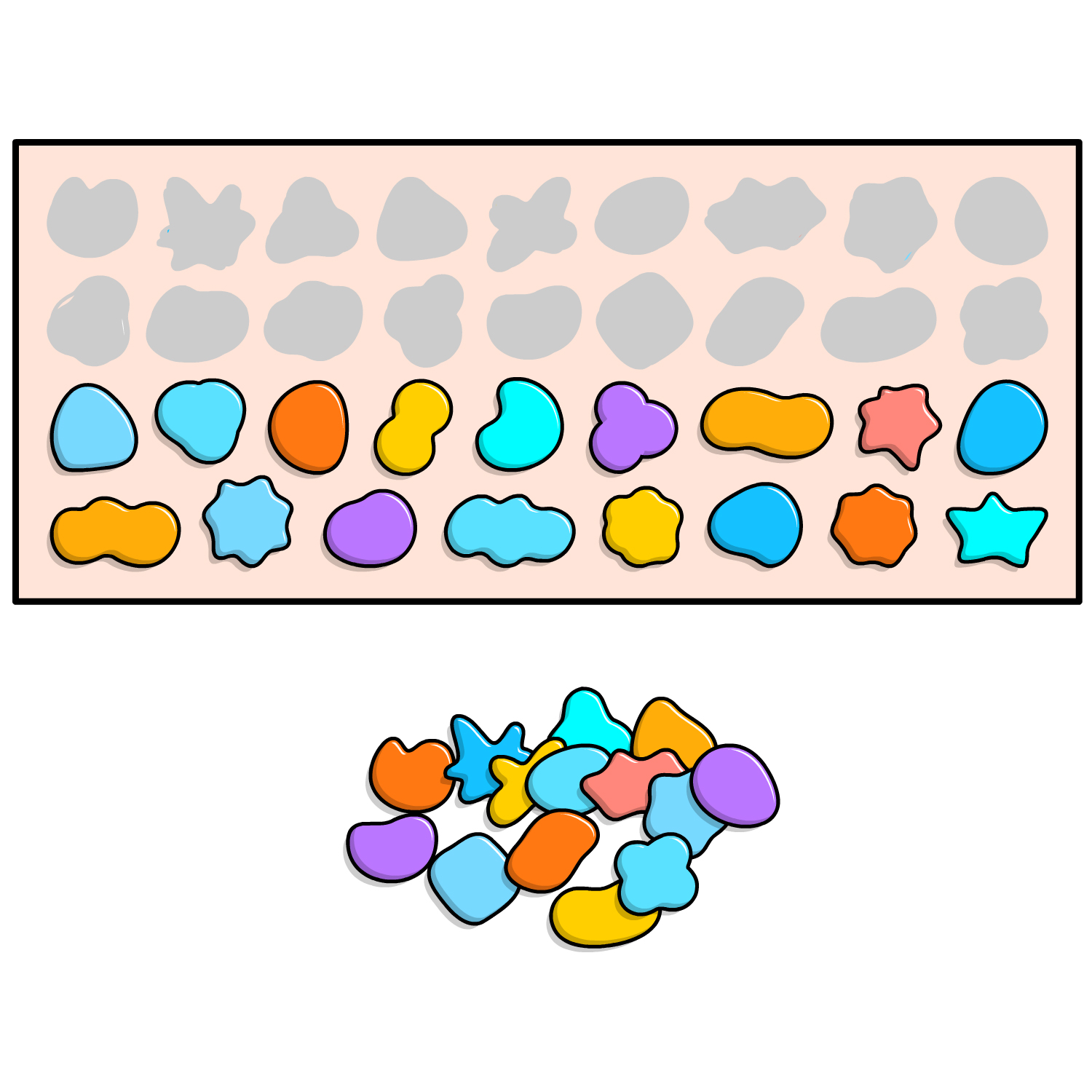 |
| 7. | Puzzles with multiple pieces which must be juxtaposed | When there is no frame, the child has to correctly juxtapose (i.e., place together) non interlocking puzzles pieces to make a pictures | 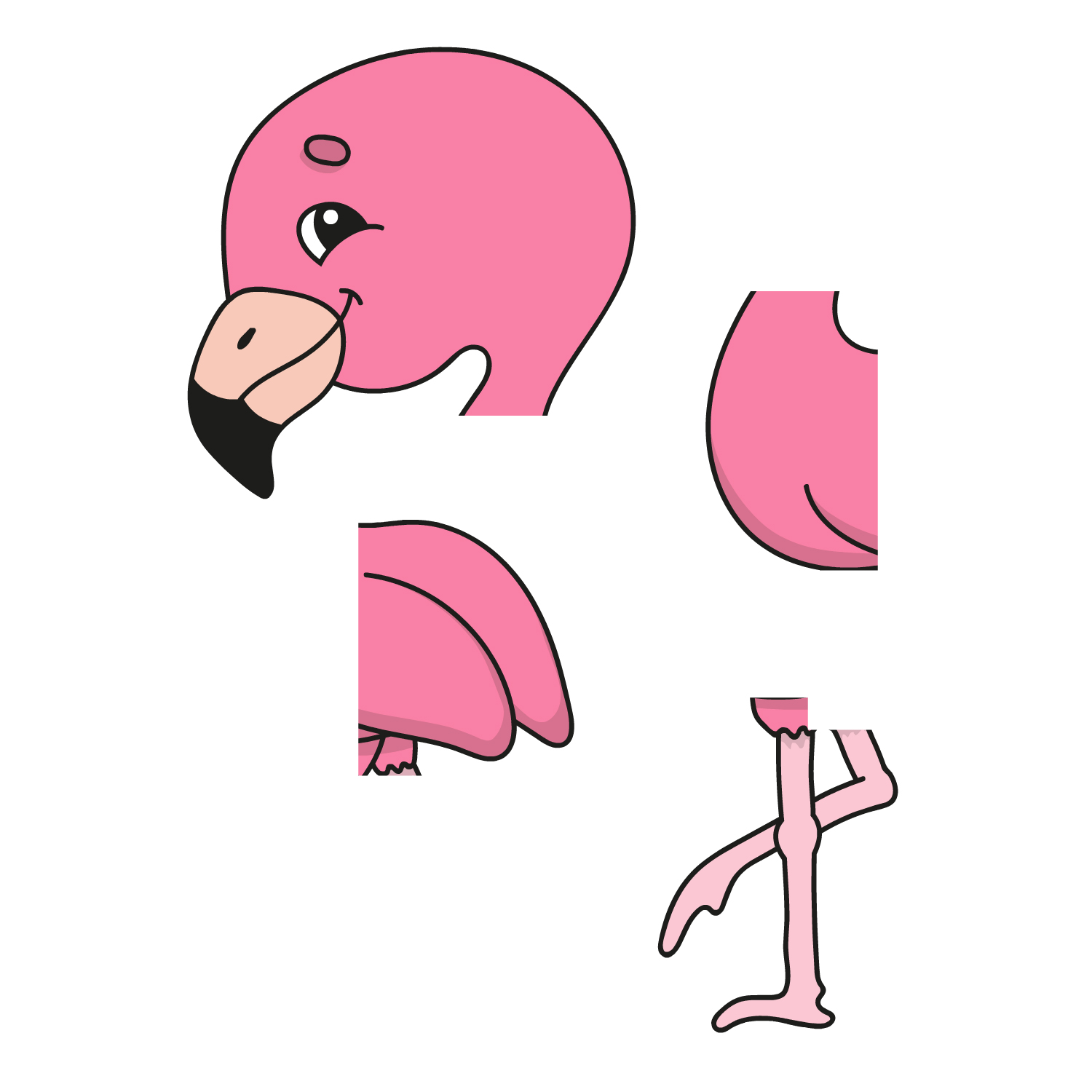 |
| 8. | Jigsaw puzzles | When given a standard jigsaw puzzles (interlocking pieces without a frame), the child has to correctly complete the puzzle |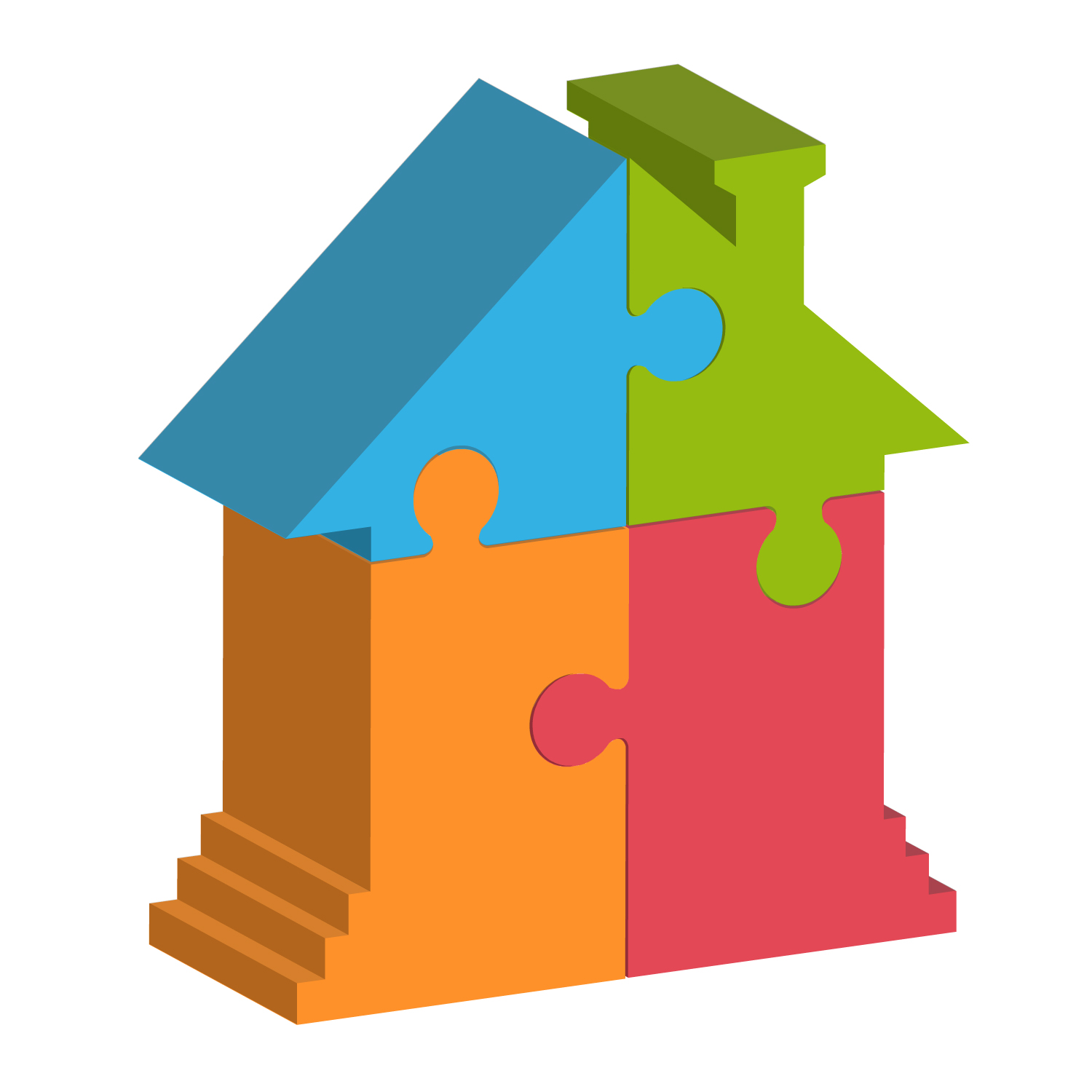  |
| 9. | Match associated pictures (ball-bat) | When provided with a display of objects or pictures, the child has to match the presented item with its associated counterpart (e.g., match a bat with the ball, a cup with a shoe) |  |
| 10. | Sort by function (blow, cutting items) | When presented with items designed for specific functions, the child must sort them into groups with similar functions (e.g., placing scissors with objects used for cutting and a pen with items used for writing). |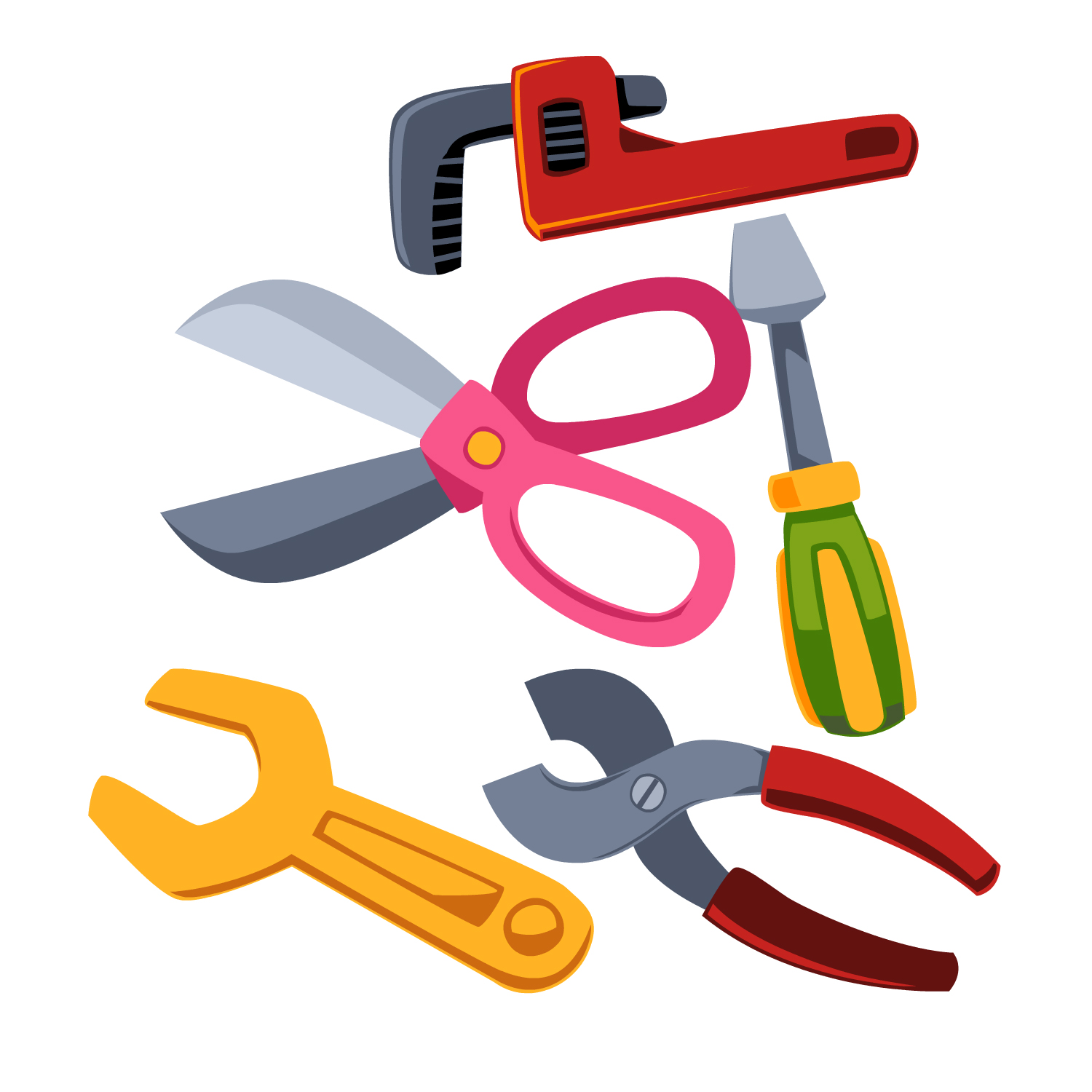  |
| 11. | Sort by features (tail, wheel, trees) | The child is given a set of items or pictures. The task involves categorizing or sorting these items into distinct groups based on specific features. |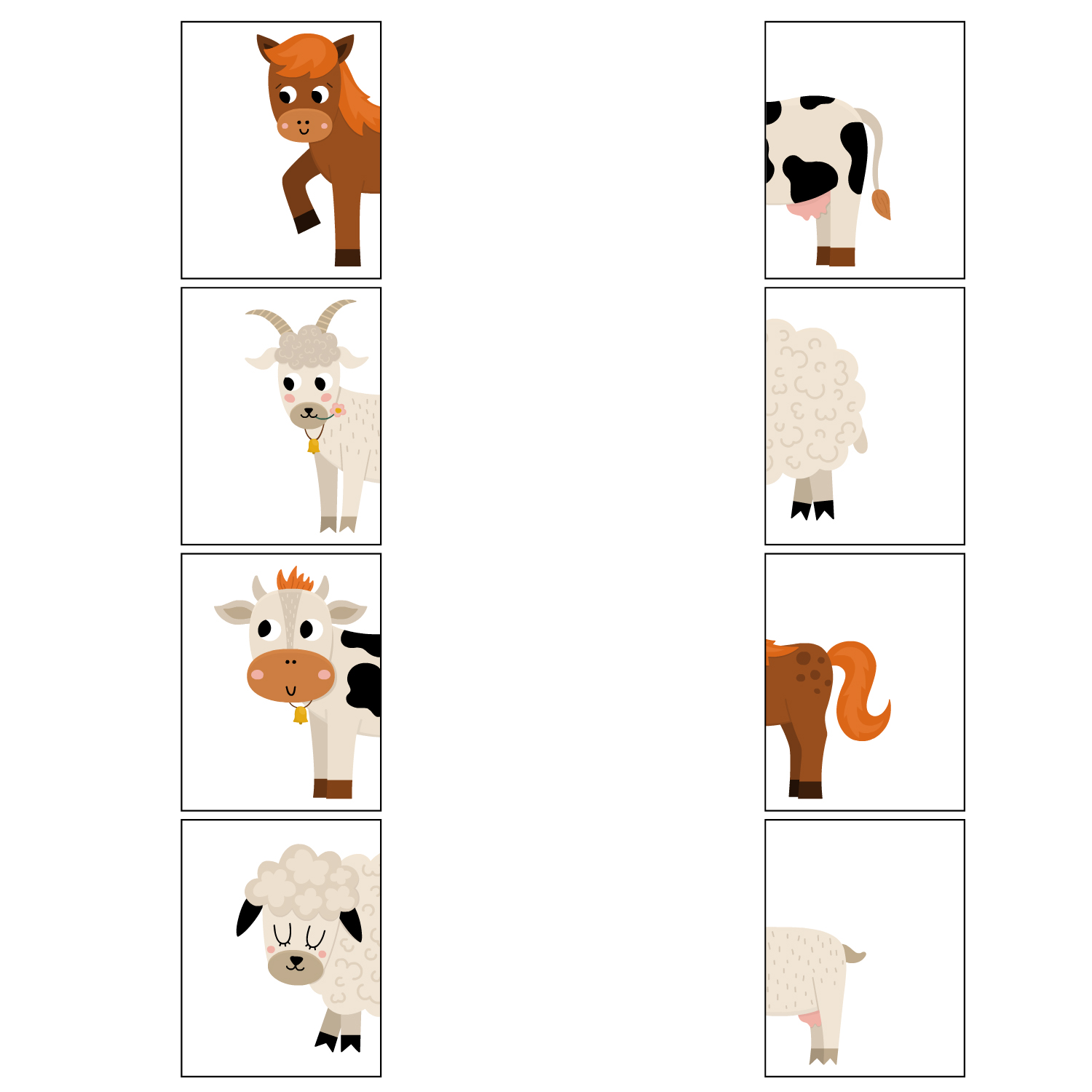  |
| 12. | Sort by class (category) | The child is presented with a collection of items or images that belong to different categories or classes. The goal of the task is to categorize or sort these items based on their shared characteristics or commonalities. |  |
Through sorting activities, children not only improve their visual discrimination and categorization skills but also develop critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Along side, integrating these tasks into a child’s routine, can significantly contribute to their overall cognitive development and readiness for more complex learning experiences.
Enhancing Language Skills Through Visual Activities
The activities mentioned in the article can indeed play a significant role in enhancing a child’s language skills and overall cognitive development. Here’s a breakdown of how these activities can benefit language development and related cognitive skills:
- Eye Contact and Social Interaction: As mentioned in the article, eye contact is crucial for social interaction. It helps children with language delays engage with others more effectively. Improved eye contact can lead to better communication and understanding of nonverbal cues, which are essential in language development.
- Visual Attention: Many of the activities, such as tracking moving objects, recognizing patterns, and following lights, promote visual attention. This skill is essential for reading, writing, and paying attention to visual details, which are all important components of language development.
- Vocabulary Building: Activities like “Stickers” and “Match associated pictures (ball-bat)” involve associating words with visual representations. This can help children expand their vocabulary by connecting words to real-world objects and concepts.
- Categorization and Sorting: Sorting activities, such as “Sort by class (category),” encourage children to categorize and group items based on common characteristics. This promotes cognitive skills related to categorization, which is fundamental for language development and word association.
- Problem-Solving: Puzzles and matching games challenge children’s problem-solving abilities. These activities require them to analyze visual information and make connections between different elements, which can improve logical reasoning and cognitive skills.
- Concentration and Attention to Detail: Engaging in activities like “Fluent matching” and “Jigsaw puzzles” requires sustained attention and concentration. These skills are valuable for language development, as they help children focus on learning and understanding language-related concepts.
- Pattern Recognition: Matching activities, especially those involving patterns, can enhance a child’s ability to recognize and understand patterns in language, which is important for reading and writing.
- Social Engagement: Many of these activities involve interaction with others, such as playing peek-a-boo or using puppets. Social engagement promotes language development by providing opportunities for verbal and nonverbal communication.
- Sequential Thinking: Some activities, like “Sequence pattern to match a visual model,” encourage children to think sequentially and arrange items in a specific order. This can translate to better organization and sequencing of words and ideas in language.
In summary, these activities can help children with language delays in several ways, including building vocabulary, improving cognitive skills, enhancing social interaction, and developing the foundational skills necessary for effective language acquisition. As a speech therapist, you can tailor these activities to meet the specific needs of each child, making them fun and engaging while focusing on language-related goals.
Conclusion: A Step Towards Holistic Development
Developing visual performance skills, particularly eye contact, is more than an educational goal; it’s a step towards holistic development. However, these skills lay the foundation for effective learning, social interaction, and overall cognitive growth. By integrating these simple yet impactful activities into daily routines, parents and educators can significantly contribute to the developmental journey of children with language delays.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are Visual Performance Skills?
Visual performance skills involve a child’s ability to use their vision effectively for learning and social interaction. This includes eye contact, tracking moving objects, recognizing patterns, and interpreting visual information. These skills are crucial for reading, writing, and engaging in social interactions.
2. How Do Visual Performance Skills Affect Learning?
Visual performance skills are foundational for academic success. They play a vital role in reading, writing, and understanding educational material. For children, especially those with language delays, strong visual skills can lead to significant improvements in communication and learning abilities.
3. Why is Eye Contact Important for Children’s Development?
Eye contact is more than a social skill. In fact, it’s a critical aspect of effective communication and learning. Moreover, it helps in understanding nonverbal cues and is particularly important for children with language delays, as it enhances their engagement and ability to interpret visual information.
4. What Activities Can Improve Eye Contact and Visual Skills in Children?
Well, activities like playing peek-a-boo, using bubbles, stencil play, and interactive games involving lights and moving objects can significantly improve a child’s eye contact and visual skills. These activities are designed to be fun and engaging, encouraging children to develop these skills naturally.
5. How Can Parents and Educators Help Children with Visual Performance Skills?
Parents and educators can support children by integrating specific activities into their daily routines. These include matching and sorting games, puzzles, and interactive play that encourage eye contact and visual tracking. Consistency and patience are key in helping children develop these skills.
6. Are Visual Performance Skills Linked to Social Development?
Yes, visual performance skills are closely linked to social development. Skills like eye contact and the ability to interpret visual cues are essential for effective social interaction and understanding others, which are important aspects of social development.
7. Can Improving Visual Skills Help Children with Language Delays?
Absolutely. For children with language delays, enhancing visual skills can lead to significant improvements in overall communication abilities. Visual cues often serve as a crucial means of understanding and interaction for these children.
8. What are Some Advanced Visual Performance Activities for Children?
Advanced activities include various types of puzzles, object-to-picture matching, and sorting exercises. These activities challenge children to use their visual skills more intensively, aiding in their cognitive development.
About the Author:
Rajini, Speech-Language Pathologist:
Rajini is a dedicated Speech-Language Pathologist with a focus on developmental speech and language disorders in children and rehabilitation in adults. With a passion for helping each individual find their voice, Rajini brings a wealth of experience and a heartfelt approach to therapy. At Wellness Hub, she’s part of a team that values innovation, compassion, and results-driven practices.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message








