Understanding Speech Delay: Causes, Milestones, and Therapy
By Rajini D
Last Updated: September 28, 2023
Speech is the basis of communication; speech refers to the physical production of sounds and words. Hence, it is the most fundamental need. We require language to communicate our thoughts, wants, and needs to others. Speech delay refers to a condition in which a child’s development of spoken language is slower than expected for their age.
Typically, children follow a predictable pattern of speech and language development, but in cases of speech delay, this progression is delayed. Communication is the broader process of exchanging information, while language is a complex system of symbols, rules, and structures used to convey meaning. Speech-language and communication are interconnected and vital for effective human interaction.
Also read : 9 Effective Exercises to Overcome Speech Delay in Toddlers
Speech and language is necessary for kids to express themselves and also to understand the world around them. Helping a child to speak, express, and understand what others say is important for them to be a good communicator that fosters learning and development. If your child is unable to produce sounds and words, then he or she cannot communicate the needs that affect their daily living and personal growth in all ways. Having good communication helps in their emotional and social well-being.
Speech refers to the physical act of producing sounds using vocal organs to form words and sentences. It involves the coordination of various muscles in the respiratory system, vocal cords, and oral cavity. Speech is essential for verbal communication and is a distinguishing feature of humans. Due to some issues like neurological conditions, biological conditions, social conditions, or maybe emotional and environmental factors, globally, more than 8% of children experience communication challenges while growing up.
What is Speech delay?
When a child doesn’t acquire the speech and language milestones according to the developmental age, then speech delay is observed. In such cases, speech therapy is needed for the child to achieve the essential speech and language milestones.
According to a study, nearly 10% of preschool children are having speech delay as a developmental issue. When children are unable to express their thoughts and wants, an emotional disturbance builds up, which increases frustration, irritation, and stubbornness in them. Hence, being able to communicate becomes a necessity for the child. It helps them to learn and grow in an emotionally healthy way.
What are Speech Milestones?
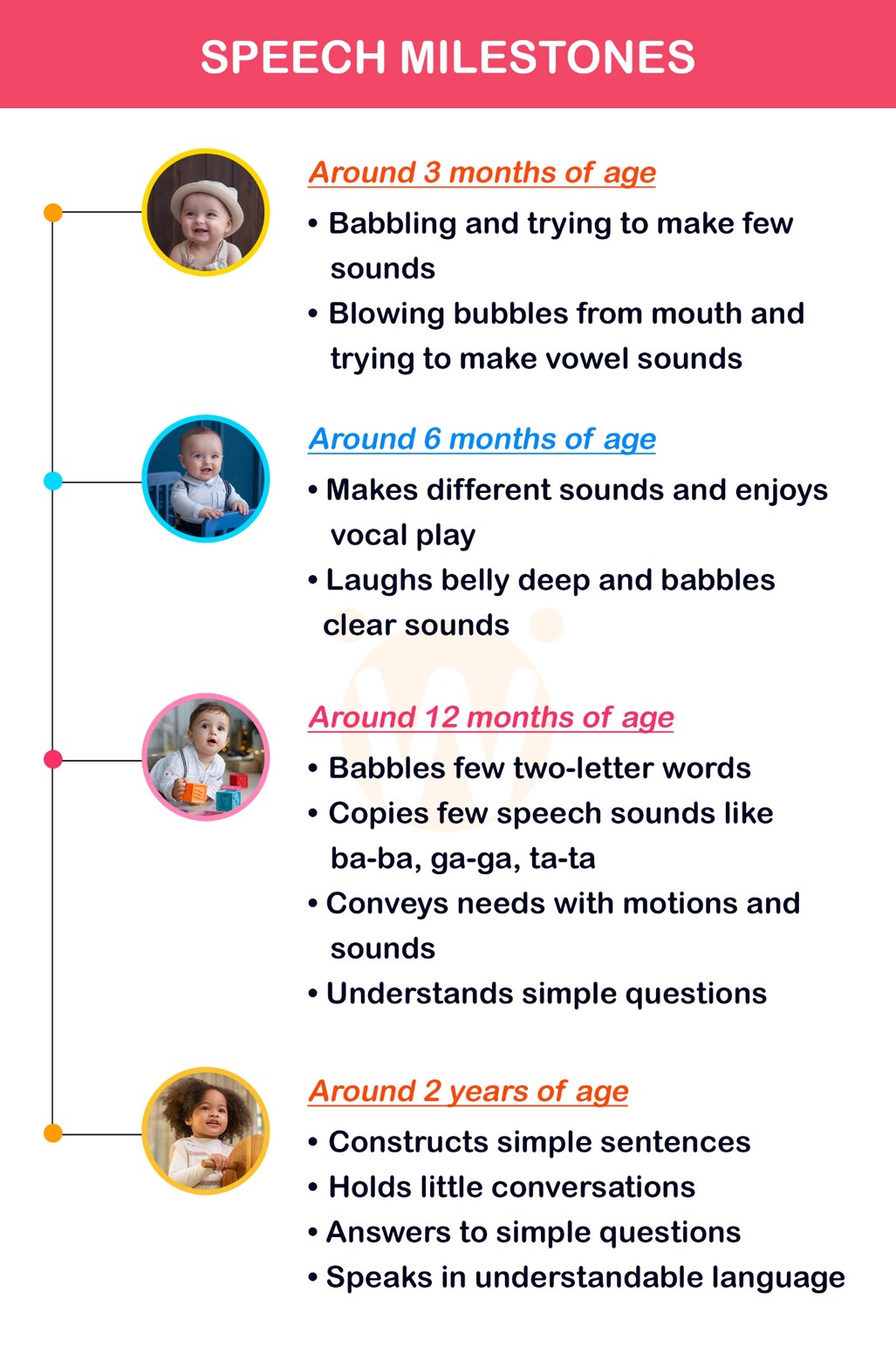
When a child doesn’t meet the speech milestones as per the chronological age, it is considered a Speech delay. The speech milestones of a normal child are
Around 3 months of age
- Babbling and trying to make a few sounds
- Blowing bubbles from the mouth and trying to make vowel sounds
Around 6 months of age
- Makes different sounds and enjoys vocal play
- Laughs belly deep and babbles clear sounds
Around 12 months of age
- Babbles a few two-letter words
- Copies of a few speeches sound like ba-ba, ga-ga, ta-ta
- Conveys needs with motions and sounds
- Understands simple questions
Around 2 years of age
- Construct simple sentences
- Holds little conversations
- Answers to simple questions
- Speaks in understandable language
Speech delay vs. language delay
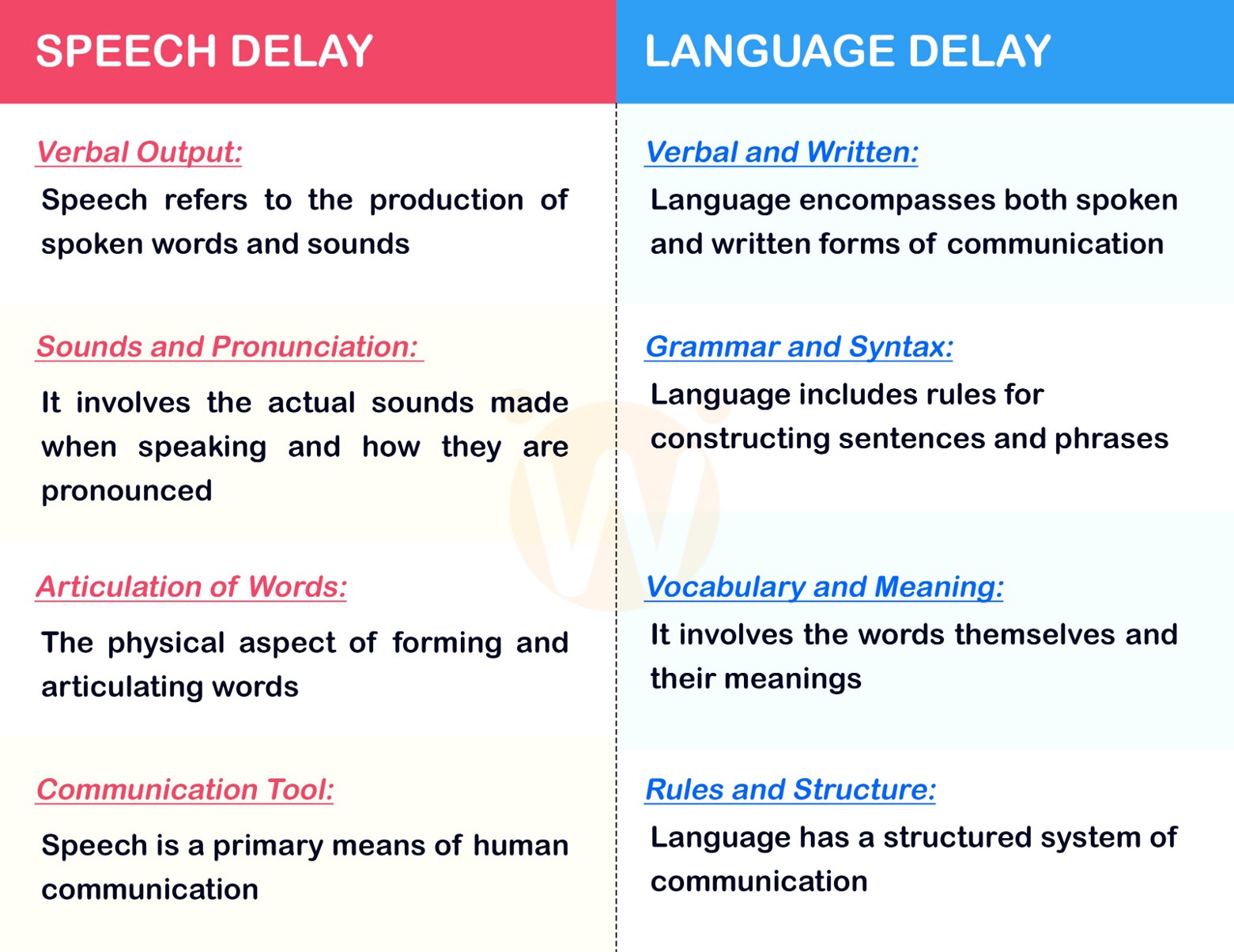
Speech and language are closely related but distinct concepts. Speech refers to the vocalized sounds that humans produce as a means of communication. Language is a complex and structured system of communication that involves the use of symbols (such as words) to convey meaning.
Speech is the oral expression of language. Speech involves the production of phonemes, which are the smallest units of sound in a language. These phonemes are combined to form words, and words are further combined to form sentences. Speech is a specific modality of communication that relies on auditory perception. It requires the listener to hear the sounds produced by the speaker and interpret their meaning, while language is a broader and more complex system that encompasses both speech and written forms of communication.
Also Read: Speech Delay vs Autism: Key Differences Explained
Language includes rules, structures, and symbols that enable humans to convey and understand meaning. While speech is one modality of language, written language (text) is another modality. People can communicate using written symbols, which are visually perceived, rather than relying on auditory perception as in speech.
A toddler with Speech delay may find it difficult to vocalize correct sounds that produce correct words. Whereas a child with language delay may pronounce words but would find it difficult to form phrases or sentences that make sense. It is common for a parent to get confused if the child has a speech delay or a language delay. It is important to meet a speech and language pathologist to get an evaluation done and to start therapies. Early intervention always helps.
Speech delay is not always the same.
Your friend’s child, who is almost the same age as your child, started speaking earlier than your little one. By two years of age, those two-letter and three-letter words start to combine, and by three years of age, simple sentences and a new vocabulary of around 1,000 words have built up. Now, you are worried about why your child is not speaking age-appropriately. Though the developmental milestones gauge a child’s progress, every child grows at their own pace. The speech milestones of each child might differ.
If your child is having a speech delay, it doesn’t always mean that something is wrong. He could be a late starter who could talk your ear off in no time. However, it is recommended to have them checked because a speech delay often indicates a hearing loss. Even if it is a small percentage, hearing loss doesn’t permit the child to learn and speak, resulting in a speech delay.
What are the causes of Speech delay in Children?
There can be many problems that cause speech delays in children. When there are problems in the areas of the brain related to speech or a structural abnormality, especially within the speech and articulatory anatomy, it can certainly contribute to speech delays in children. Examples of such oral-motor issues include
- Cleft lip and palate
- Tongue-tie
- Velopharyngeal dysfunction
- Dental issues
- Tongue thrust
- Weak oral muscles
- Structural differences in articulators
- Apraxia of speech
- Dysarthria
Children with such issues find it difficult to coordinate between jaw muscles, lips, and tongue. This is also evident during the feeding process. Due to this miscoordination, some speech sounds are mispronounced. Along with that, there are other issues that hinder speech progress in children, such as
- Hearing loss
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Intellectual disability
- Developmental delay
- Cerebral Palsy
Apart from all these neurological conditions, psychosocial factors like “Selective Mutism” are also a major factor for speech delay in children.
Selective Mutism
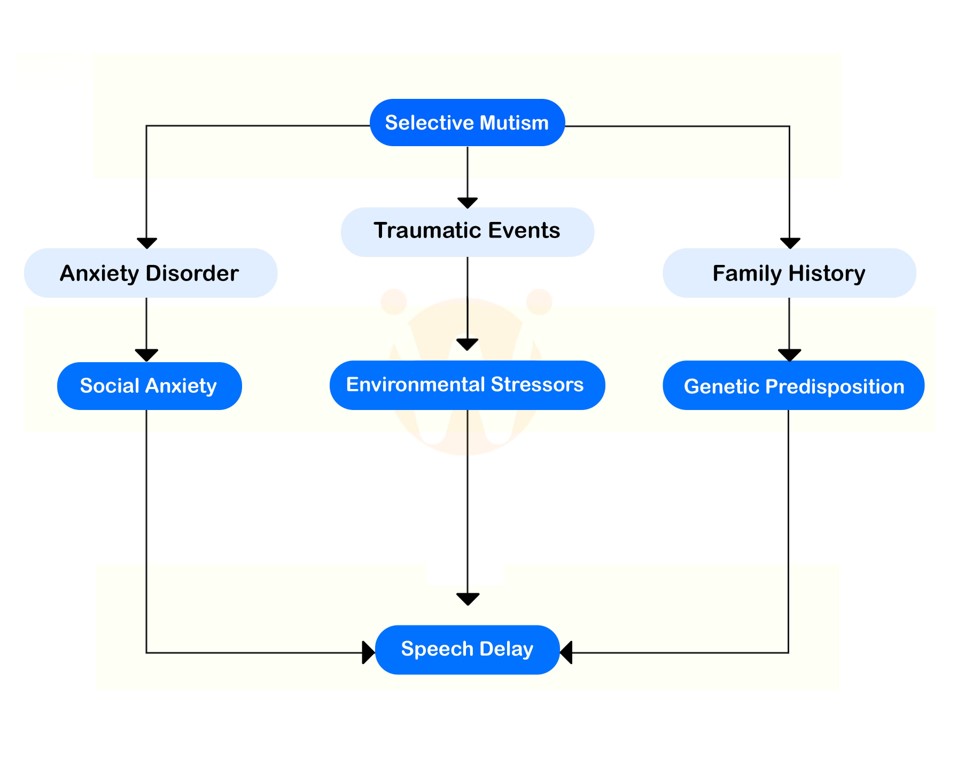
Selective mutism is a state where the child chooses to stay silent despite being able to speak. These kids remain silent in certain settings or with certain people. It can be observed when a child doesn’t want to interact with a stranger, doesn’t want to go to school, or has separation anxiety. This can also be seen when the child goes through some traumatic events or abusive situations.
Does your child need Speech Therapy?
The need for speech therapy can be identified at an early age. Even before a child says their first word, there are certain non-verbal cues to identify if the child is communicative or not. Some of those early signs include the following.
- Having joint attention: The child can have shared attention on the object with another person.
- Eye contact: The child maintains eye contact and responds to your gestures, voice, and sounds
- Easily engaged: The child is easily engaged in play activities.
- Tries to vocalize or babble: The child tries to babble sounds like baba/tata/Mimi or so while responding.
- Active response: The child actively responds to sounds or name calls. Though they avoid it once or twice, you can see the other times.
If such age-appropriate milestones are not met, some behavioral issues will arise in the child. These issues will slowly increase if the speech is not improved at an early age.
If you observe that the child has not achieved speech milestones, it is advisable to consult an audiologist and speech-language pathologist. For example, if the child is not speaking at least two-letter words by 2 years of age, then it is good to have a check. The audiologist checks for hearing issues, if any. The speech therapist will assess structural and functional abnormality, if any. The speech therapist designs therapy according to the child’s speaking level. A Speech therapist tailors a therapy plan according to the child’s needs after a detailed speech assessment.
How does Speech Therapy help?
Speech therapy focuses on working with the child after the problem areas are identified. A Speech therapist will chalk out a therapy plan according to the necessities of your child to improve their speech and language skills. Accordingly, the SLP (speech and language pathologist) or speech therapist will plan the curriculum for the sessions. Your speech therapist or SLP focuses on
- Receptive language (what the child understands)
- Expressive language (what the child expresses)
- Clarity of speech (mispronunciations, if any)
- Coordination of jaw, tongue, and mouth (how the child chews and swallows the food; how the movement supports speech and improves it)
- Exercises that improve speech quality
We will guide you on all the Dos and Don’ts that help the kid cope faster. It also provides you with the material and exercises to do at home that help the therapy continue. Before the therapy starts, our therapist lists out the target date and goals, which can be easily accessible on the website. This helps the parents in tracking the progress of the child. Introducing speech apps during and after therapy sessions can aid the kid’s learning process.
Our psychologists can provide emotional support for the caregivers and the families of children with speech issues. Our speech support app helps patients continue therapy even after the therapy sessions. Early intervention programs at Wellness Hub provide personalized care at an early stage of speech issues. Group therapies play a vital role in enhancing social communication skills. Parents or caregivers are educated about speech and language milestones and are taught strategies to support their child’s progress at home. Regular tracking of progress and improvement of the therapy plan according to the child’s progress are part of the curriculum. This collaborative approach ensures a holistic approach to development.
Conclusion
speech delay is a condition where a child does not meet expected speech and language developmental milestones. It’s important for parents and caregivers to be aware of these milestones to recognize early signs of potential delays. Various factors, including neurological issues, structural abnormalities, and social or emotional conditions, can contribute to speech delays. Early detection and intervention through speech therapy are crucial as they greatly enhance the likelihood of improvement. Engaging in speech-enhancing activities at home and seeking professional guidance when necessary are effective ways to support a child’s communication development. Speech therapy not only helps improve speech and language skills but also boosts a child’s confidence and social interaction capabilities
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is speech delay?
Speech delay occurs when a child doesn’t acquire speech and language milestones according to their developmental age. Speech therapy may be required to help the child achieve these essential milestones.
2. What are common speech milestones for children?
Speech milestones include babbling and making sounds at 3 months, enjoying vocal play at 6 months, babbling two-letter words at 12 months, and constructing simple sentences by 2 years of age.
3. How do speech delay and language delay differ?
Speech delay involves difficulties in producing vocal sounds, while language delay involves difficulties in forming coherent phrases or sentences, even if words are pronounced correctly.
4. What causes speech delay in children?
Causes can include neurological issues, structural abnormalities in the speech and articulatory anatomy, hearing loss, autism spectrum disorders, intellectual disabilities, and psychosocial factors like selective mutism.
5. How can I tell if my child might have a speech delay?
Early signs include a lack of babbling, limited use of gestures to communicate, poor response to sounds, and difficulty with eye contact or joint attention.
6. Does every child with speech delay need speech therapy?
Not all children with speech delays require therapy, but it’s recommended to have them evaluated by a speech-language pathologist if there are concerns about their speech development.
7. What does speech therapy for children involve?
Speech therapy can include exercises to improve the clarity of speech, coordination of jaw, tongue, and mouth, and both receptive (understanding) and expressive (speaking) language skills.
8. What are some exercises recommended for overcoming speech delay in toddlers?
Exercises can include activities that enhance vocal play, improve articulation and phonetics, and strengthen oral muscles, as well as interactive reading and singing.
9. How can parents support their child’s speech development at home?
Parents can engage in regular talking, reading, and singing with their children, respond to their attempts at communication, and use clear, simple language to model proper speech.
10. What is the role of group therapies in speech delay?
Group therapies help enhance social communication skills among children with speech delays by providing opportunities to interact with peers and practice communication in a supportive environment.
About the Author:
Rajini Darugupally
M.Sc., Speech-Language Pathologist (9+ years of experience)
Rajini is a passionate and dedicated Speech-Language Pathologist with over 9+ years of experience, specializing in both developmental speech and language disorders in children and rehabilitation in adults. Driven by a desire to empower each individual to find their voice, Rajini brings a wealth of experience and a warm, genuine approach to therapy.
Currently, at Wellness Hub, she thrives in a team environment that values innovation, compassion, and achieving results for their clients.
Connect with Rajini to learn more about how she can help you or your loved one find their voice.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message









