Mastering Alveolar Sounds in Children: A Parent’s Guide
By Rajini D
Last Updated: March 9, 2024
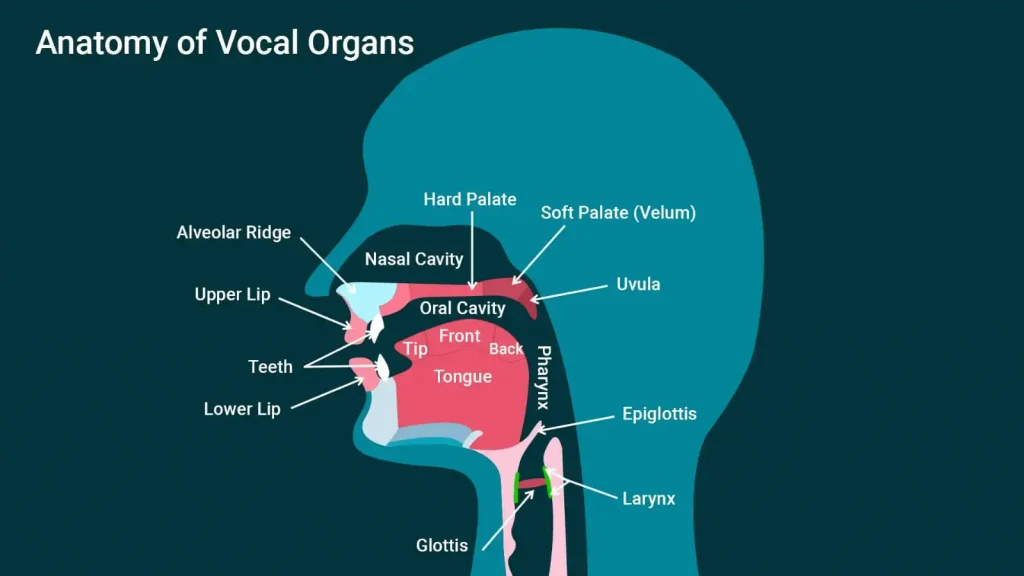
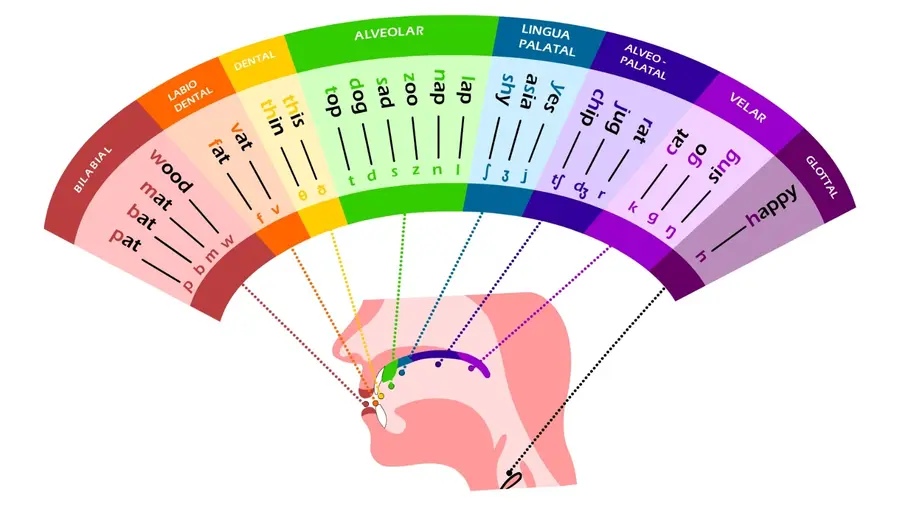
Alveolar sounds are key components of speech and language development in children. These sounds involve the use of the tongue against the alveolar ridge, located just behind the upper front teeth. Common alveolar sounds in English include /t/, /d/, /s/, /z/, /n/, /l/, and /r/, as found in “top,” “dog,” “sat,” “zoo,” “nap,” “lap,” and “rat,” respectively. Children typically master these sounds around the ages of 3 to 6 years. Proper development of these sounds is crucial for clear speech and effective communication skills.
Book Free Speech Therapy Consultation.
Understanding Alveolar Sounds
Defining Alveolar Sounds:
Alveolar sounds are made by placing the tip of the tongue against the alveolar ridge. They play a significant role in speech across various languages. The sounds /t/, /d/, /s/, /z/, /n/, /l/, and /r/ are primary examples, each with unique characteristics:
- /t/ is a voiceless sound, produced without vocal cord vibration.
- /d/ is its voiced counterpart, produced with vocal cord vibration.
- /s/ and /z/ are sibilants, with /s/ being voiceless and /z/ being voiced.
- /n/ is a nasal sound, allowing air to flow through the nose.
- /l/ is a lateral sound, where air flows along the sides of the tongue.
- /r/ is characterized by a specific tongue placement and is often considered one of the more challenging sounds.
For more information on speech and language milestones, check out our detailed guide.
Techniques for Teaching Alveolar Sounds
Technique 1: Articulation Therapy Progression
Syllables to Words:
Start with simple syllables like “ta”, “te”, “ti”. Progress to more complex syllables and words, such as “top”, “dog”, and “sat”.
Words to Sentences:
Once individual sounds and words are mastered, form short sentences to enhance speaking ability.
Technique 2: Tactile and Kinesthetic Cues
Physical Cues for Each Sound:
Teach children the correct tongue placement and breath control for each sound, such as guiding their tongue for /t/ and /d/ sounds.
Also Read: Home-Based Occupational Therapy Activities.
Technique 3: Visual and Auditory Support
Visual Articulation Cards:
Use visual aids illustrating tongue and palate positions for each alveolar sound, aiding in understanding their physical production.
Auditory Repetition Exercises:
Regularly practicing these sounds in different contexts reinforces learning.
Discover more about what to expect in speech and language development at these ages by reading about 2 to 3-year milestones and 3 to 4-year milestones.
Specific Practices for Each Alveolar Sound
The /t/ Sound
Teaching Steps:
- Tongue Placement: Teach the child to place the tip of their tongue against the alveolar ridge.
- Breath Control: Instruct them to release air sharply, creating the /t/ sound.
- Practice: Start with the /t/ sound, then syllables like “ta,” “we,” and “ti,” and words like “top,” “tick,” and “bat.”
The /d/ Sound
Teaching Steps:
- Voice Vibration: Unlike /t/, /d/ is voiced. Teach the child to feel the vibration in their throat.
- Tongue Placement: Similar to /t/ but with vocal cord vibration.
- Comparison with /t/: Demonstrate the difference between the two sounds.
The /s/ and /z/ Sounds
Teaching Steps:
- Sibilant Quality: Teach that /s/ and /z/ are sibilant sounds characterized by a hissing quality.
- Tongue Placement: The tongue should be close to the alveolar ridge without touching it.
- Voice Vibration: /s/ is voiceless, and /z/ is voiced.
The /n/ Sound
Teaching Steps:
- Nasal Quality: Explain that the sound resonates in the nose.
- Tongue Placement: The tip of the tongue touches the alveolar ridge.
- Humming: Start with humming to feel the nasal vibration, then transition to /n/ sounds in words like “nap”, “run”.
The /l/ Sound
Teaching Steps:
- Lateral Quality: Air should flow along the sides of the tongue.
- Tongue Placement: The tip of the tongue touches the alveolar ridge, with the sides of the tongue lowered.
- Practice: Begin with “la”, “le”, “li”, and words like “lap”, “lull”, “ball”.
The /r/ Sound
Teaching Steps:
- Rhotic Quality: Teach the unique tongue positioning for /r/.
- Tongue Placement: The tongue should be curled back or bunched, depending on the accent.
- Practice: Begin with “ra”, “re”, “ri”, and words like “rat”, “ring”, “car”.
If your child is on the autism spectrum and experiencing speech delays or atypical phonological processes, learn about our Speech Therapy for Autism.
Advanced Practice and Word Lists
For each sound, create word lists that practice the sound in initial, final, and medial positions. Include a range of words from simple to complex structures. For example:
The /t/ Sound:
- Syllable Combinations: Practice combining /t/ with various vowels – ta, te, ti, to, tu.
- Drills: Practice with pairs like “tat-bat”, “till-bill”, “tight-bite” to distinguish /t/ from other sounds.
- Word List for /t/ sound: Practice /t/ sound in Initial, Final, and Medial position of a word.
Word List for /t/ sound:
/t/ Sound in the Initial Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Tap, tan, tab, tack, task, trash, track
- ‘e’ vowel: Ten, test, tell, tent, tech, tepid, text
- ‘i’ vowel: Tip, tin, tick, till, tinsel, tint, tilt
- ‘o’ vowel: Top, ton, toss, tomb, tock, totem, toll
- ‘u’ vowel: Tub, tug, tuck, tuff, tusk, tulle, turf
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Trust, tramp, trick, trinket, trunk, trump, thrust
- CCVC: Twist, twang, trend, trunk, throng, throb, truss
- CVVC: Treat, troop, truce, trail, trawl, tweed, trout
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Translate, transmit, terrific, tectonic, tolerate, turbulent, transcend
/t/ Sound in Final Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Bat, hat, mat, pat, rat, sat, fat
- ‘e’ vowel: Bet, let, met, net, pet, set, vet
- ‘i’ vowel: Bit, hit, kit, lit, pit, sit, wit
- ‘o’ vowel: Bot, cot, dot, got, hot, lot, pot
- ‘u’ vowel: But, cut, hut, jut, nut, rut, tut
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Blast, crust, drift, ghost, thirst, twist, wrist
- CCVC: Brunt, grant, plait, quilt, tryst, spelt, throb
- CVVC: Boat, coat, float, goat, moat, throat, vote
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Abstract, biscuit, closet, deposit, insect, market, secret
/t/ Sound in the Medial Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Bathe, lathe, path, math, bath, lath, wrath
- ‘e’ vowel: Biter, later, meter, peter, tether, nether, setter
- ‘i’ vowel: Biting, citing, lighting, fighting, kiting, sighting, writing
- ‘o’ vowel: Botany, pottery, lottery, rotter, blotter, hotter, plotter
- ‘u’ vowel: Butane, cuter, muter, putter, shutter, flutter, utter
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Button, mutton, bitten, cotton, kitten, rotten, smitten
- CCVC: Attain, attain, attempt, attend, attack, attire, attain
- CVVC: Beauty, duty, booty, cutie, fruity, rooty, tooty
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Attempting, attentive, automatic, certificate, integrity, maternity, opportunity
The /d/ Sound:
- Syllable Combinations: Practice combining /d/ with various vowels – da, de, di, do, du.
- Drills: Practice with pairs like “dad-bad”, “did-bid”, “dote-boat” to distinguish /d/ from other sounds.
- Word List for /d/ sound: Practice /d/ sound in Initial, Final, and Medial position of a word.
Word List for /d/ sound:
/d/ Sound in the Initial Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Dad, dam, dab, dack, dash, dad, dank
- ‘e’ vowel: Den, desk, dell, dent, deck, depth, dex
- ‘i’ vowel: Dip, din, dick, dill, dish, dint, dink
- ‘o’ vowel: Dog, don, doll, dock, dogma, dot, doll
- ‘u’ vowel: Dud, dug, duck, duff, dusk, dull, dump
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Drift, drab, drink, drock, drum, drump, drest
- CCVC: Dwarf, dwindle, dwell, dwest, dwrap, drench, droll
- CVVC: Dream, droop, drupe, drain, droid, drew, drool
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Dedicate, decimal, decorate, dynamic, dominate, durable, derivate
/d/ Sound in Final Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Bad, had, mad, pad, rad, sad, fad
- ‘e’ vowel: Bed, led, med, ned, ped, sed, ved
- ‘i’ vowel: Bid, hid, kid, lid, pid, sid, wid
- ‘o’ vowel: Bod, cod, dod, god, hod, lod, pod
- ‘u’ vowel: Bud, cud, hud, jud, nud, rud, sud
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Brand, grand, blend, end, hand, land, sand
- CCVC: Bread, dread, freed, greed, plead, read, seed
- CVVC: Brood, crude, dude, feud, mood, rude, sued
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Absurd, candid, rapid, splendid, timid, valid, avid
/d/ Sound in Medial Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Ladder, madden, padden, raddle, saddle, adder, badder
- ‘e’ vowel: Middler, peddle, reddle, meddle, heddle, fiddle, puddle
- ‘i’ vowel: Hidden, ridden, kidded, midded, bidden, lidded, giddied
- ‘o’ vowel: Poodle, noodle, moddle, roddle, toddle, waddle, yodel
- ‘u’ vowel: Puddle, muddle, fuddle, huddle, cuddle, ruddle, buddle
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Addict, eddied, oddity, undid, middling, riddled, puddling
- CCVC: Addend, eddish, idiom, oddest, udder, addle, educe
- CVVC: Audio, educe, iodine, odious, udder, adduce, edify
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Candidate, meditate, individual, sediment, administer, paradox, candidate
The /n/ Sound:
- Syllable Combinations: Practice combining /n/ with various vowels – na, ne, ni, no, nu.
- Drills: Practice with pairs like “nap-map”, “net-met”, “nite-bite” to distinguish /n/ from other sounds.
- Word List for /n/ sound: Practice /n/ sound in Initial, Final, and Medial position of a word.
Word List for /n/ sound:
/n/ Sound in Initial Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Nan, nap, nab, nack, nash, nad, nank
- ‘e’ vowel: Nen, nest, nell, nent, neck, neth, nex
- ‘i’ vowel: Nip, nin, nick, nill, nish, nint, nink
- ‘o’ vowel: Nog, non, noll, nock, nogma, not, noll
- ‘u’ vowel: Nun, nug, nuck, nuff, nusk, null, nump
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Nrift, nrab, nrink, nrock, nrum, nrump, nrest
- CCVC: Nwarf, nwindle, nwelt, nwest, nwrap, nrench, nroll
- CVVC: Nream, nroop, nrupe, nrain, nroid, nrew, nrool
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Nidicate, nedimal, necorate, nynamic, nominate, nurable, nerivate
/n/ Sound in Final Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Ban, han, man, pan, ran, san, fan
- ‘e’ vowel: Ben, len, men, nen, pen, sen, ven
- ‘i’ vowel: Bin, hin, kin, lin, pin, sin, win
- ‘o’ vowel: Bon, con, don, gon, hon, lon, pon
- ‘u’ vowel: Bun, cun, hun, jun, nun, run, sun
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Brand, grand, blend, end, hand, land, sand
- CCVC: Brain, drain, freen, green, plain, rain, seen
- CVVC: Boon, croon, dune, foon, moon, roon, soon
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Absurdn, candidn, rapidn, splendidn, timidn, validn, avidn
/n/ Sound in the Medial Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Banner, manner, panner, rannel, sannel, anner, banner
- ‘e’ vowel: Minder, pender, render, mender, hender, finder, pundle
- ‘i’ vowel: Binning, winning, pinning, minning, binning, linner, ginning
- ‘o’ vowel: Ponder, nonder, monder, ronder, tonder, wander, yonder
- ‘u’ vowel: Punder, munder, funder, hunder, cunner, runner, bundler
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Annict, endied, ondity, undid, minnling, rinnled, punnling
- CCVC: Annect, eddish, innect, onnect, unner, annle, ennuse
- CVVC: Aunio, enuce, ionine, onious, unner, annuce, enify
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Connebrate, innebrate, innection, nennection, anninister, ponadox, connidate
The /l/ Sound:
- Syllable Combinations: Practice combining /l/ with various vowels – la, le, li, lo, lu.
- Drills: Practice with pairs like “lap-map”, “let-met”, “light-might” to distinguish /l/ from other sounds.
- Word List for /l/ sound: Practice /l/ sound in Initial, Final, and Medial position of a word.
Word List for /l/ sound:
/l/ Sound in Initial Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Lad, lam, lab, lack, lash, lad, lank
- ‘e’ vowel: Led, less, sell, lent, leck, leth, lex
- ‘i’ vowel: Lip, lin, lick, lill, lish, lint, link
- ‘o’ vowel: Log, lon, loll, lock, logma, lot, loll
- ‘u’ vowel: Lud, lug, luck, luff, lusk, lull, lump
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Lift, lamb, link, lock, lump, lumb, lest
- CCVC: Clasp, fling, pluck, slink, blink, clank, plank
- CVVC: Leach, loom, lute, lain, loon, lewd, loot
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Legalize, laminate, levitate, limerick, localize, luminous, literate
/l/ Sound in Final Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Bal, hal, mal, pal, ral, sal, fal
- ‘e’ vowel: Bel, lel, mel, nel, pel, sel, vel
- ‘i’ vowel: Bil, hil, kil, lil, pil, sil, wil
- ‘o’ vowel: Bol, col, dol, gol, hol, lol, pol
- ‘u’ vowel: Bul, cul, hul, jul, nul, rul, sul
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Brill, grill, still, trill, skill, spill, quill
- CCVC: Blare, clare, flare, glare, plare, slare, thral
- CVVC: Bloat, cloak, fluke, gloom, plume, sloot, true
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Angelical, biblical, clinical, digital, ethical, logical, musical
/l/ Sound in Medial Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Baller, mallet, pallet, rally, sally, aller, bally
- ‘e’ vowel: Miller, peller, rellow, mellow, heller, filler, pulley
- ‘i’ vowel: Billing, willing, killing, milling, billing, lilly, gilling
- ‘o’ vowel: Pollen, nollen, mollen, rollen, tollen, wallow, yellow
- ‘u’ vowel: Puller, muller, fuller, huller, culler, ruller, buller
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Ballet, felled, molten, sullen, gulley, pullet, mallet
- CCVC: Allure, ellipse, illume, oliver, ulster, allic, elicit
- CVVC: Aulio, elude, ilium, olium, ulna, alluce, elife
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Collateral, illuminate, bilingual, melancholy, alleviate, collateral, analytical
The /s/ Sound:
- Syllable Combinations: Practice combining /s/ with various vowels – sa, se, si, so, su.
- Drills: Practice with pairs like “sat-mat”, “sell-bell”, “sight-bite” to distinguish /s/ from other sounds.
- Word List for /s/ sound: Practice /s/ sound in Initial, Final, and Medial position of a word.
Word List for /s/ sound:
/s/ Sound in Initial Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Sap, san, sab, sack, sash, sand, sank
- ‘e’ vowel: Set, sent, sell, sect, seck, septic, sex
- ‘i’ vowel: Sip, sin, sick, sill, silt, sint, sink
- ‘o’ vowel: Sop, son, sob, sock, somber, sot, sol
- ‘u’ vowel: Sub, sum, suds, suck, suff, sulk, sun
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Scamp, script, skulk, splint, spunk, squib, scrub
- CCVC: Sclera, smear, snare, spire, spruce, square, squire
- CVVC: Seize, soup, sue, sail, soil, suit, swoon
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Saturate, signify, silhouette, systematic, simulate, suffocate, substantial
/s/ Sound in Final Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Bas, has, mas, pas, ras, sas, fas
- ‘e’ vowel: Bes, les, mes, nes, pes, ses, ves
- ‘i’ vowel: Bis, his, kis, lis, pis, sis, wis
- ‘o’ vowel: Bos, cos, dos, gos, hos, los, pos
- ‘u’ vowel: Bus, cus, hus, jus, nus, rus, sus
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Crisp, clasp, risk, mask, dusk, husk, tusk
- CCVC: Brass, crass, dress, glass, press, truss, bliss
- CVVC: Cease, goose, house, moose, noise, ruse, tease
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Emphasis, genesis, oasis, precise, release, surplus, thesis
/s/ Sound in Medial Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Basal, nasal, pass, mass, lasso, gasp, raspy
- ‘e’ vowel: Beset, reset, fester, pester, tester, nestle, wrestle
- ‘i’ vowel: Miser, visor, riser, hiss, kisser, miss, bliss
- ‘o’ vowel: Poser, loser, mosey, possum, rosy, cozy, nosy
- ‘u’ vowel: Usurp, musket, bust, dust, gusto, just, rust
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Basque, musk, risk, husk, tusk, desk, whisk
- CCVC: Ascend, escape, isotope, osprey, usurp, eschew, isle
- CVVC: Assume, easel, isle, ooze, use, easel, issue
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Assemble, decisive, disastrous, masonry, necessity, passive, versatile
The /z/ Sound:
- Syllable Combinations: Practice combining /z/ with various vowels – za, ze, zi, zo, zu.
- Drills: Practice with pairs like “zat-bat”, “zeal-peel”, “zoo-due” to distinguish /z/ from other sounds.
- Word List for /z/ sound: Practice /z/ sound in Initial, Final, and Medial position of a word.
Word List for /z/ sound:
/z/ Sound in Initial Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Zap, zan, zab, zack, zash, zand, zank
- ‘e’ vowel: Zen, zest, zell, zent, zech, zephyr, zex
- ‘i’ vowel: Zip, zin, zick, zill, zilt, zint, zink
- ‘o’ vowel: Zop, zon, zob, zock, zomber, zot, zol
- ‘u’ vowel: Zub, zum, zuds, zuck, zuff, zulk, zun
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Zest, zinc, zlack, zlock, zlump, zlumb, zlest
- CCVC: Zlant, zleer, znare, zpire, zpruce, zquare, zquire
- CVVC: Zease, zoop, zue, zail, zoil, zupe, zwoon
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Zaturate, zignify, zilhouette, zystematic, zimulate, zuffocate, zubstantial
/z/ Sound in Final Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Baz, haz, maz, paz, raz, saz, faz
- ‘e’ vowel: Bez, lez, mez, nez, pez, sez, vez
- ‘i’ vowel: Biz, hiz, kiz, liz, piz, siz, wiz
- ‘o’ vowel: Boz, coz, doz, goz, hoz, loz, poz
- ‘u’ vowel: Buz, cuz, huz, juz, nuz, ruz, suz
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Blizz, fuzz, buzz, jazz, whizz, frizz, muzz
- CCVC: Bras, cras, dres, gras, pres, tras, blas
- CVVC: Booz, chooz, fuze, gooze, mooze, rooze, sooze
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Amaze, analyze, criticize, legalize, memorize, prioritize, visualize
/z/ Sound in Medial Position of a Word
CVC Words
- ‘a’ vowel: Bazaar, hazard, puzzle, dazzle, nozzle, gizmo, razzle
- ‘e’ vowel: Buzzer, fezzer, mezzo, pezzy, tezzle, nezzle, wezzle
- ‘i’ vowel: Mizzle, drizzle, frizzle, sizzle, tizzy, whizzy, dizzy
- ‘o’ vowel: Nozzle, doze, bozo, pozzle, cozy, mozy, rozy
- ‘u’ vowel: Buzzard, muzzle, buzz, fuzz, guzzle, juzzle, ruzzle
More Complex Syllable Structures
- CVCC: Fizz, jazz, buzz, whizz, frizz, fizz, muzz
- CCVC: Bizarre, disband, fizzup, nozzle, puzzle, razzer, tizzup
- CVVC: Ooze, azure, seizure, leisure, fusion, visual, resize
Additional Words
- Varied syllables: Amaze, buzzword, drizzle, sizzle, dazzle, nozzle, puzzle
Learn more about Autism Spectrum Disorder and its therapies.
Explore our dedicated autism treatment centre in Hyderabad for comprehensive care.
Using Books and Everyday Activities
Choose books rich in alveolar sounds and incorporate these sounds into daily activities. Emphasize and repeat the alveolar sounds in an engaging manner. For example:
Book Recommendations by Sound:
| Sound | Book Title | Key Words |
|---|---|---|
| /t/ | “The Tiny Seed” by Eric Carle “Teddy Bear, Teddy Bear” | dirt, tall |
| /d/ | “Madeline” by Ludwig Bemelmans | door, lady |
| /s/ | “The Snake Who Said Shhh” by Jodie Parachini | soap, grass |
| /z/ | “My Friends” by Taro Gomi “Zoo Looking” | |
| /n/ | “One Fish, Two Fish, Red Fish, Blue Fish” by Dr. Seuss | nine, funny |
| /l/ | “Llama Llama Red Pajama” by Anna Dewdney | llama, play |
| /r/ | “The Rainbow Fish” by Marcus Pfister | rainbow, rock |
Conclusion
Understanding and mastering alveolar sounds is vital for a child’s language development. Recognizing the typical age for mastering these sounds and identifying challenges early can lead to effective interventions. This comprehensive approach ensures a strong foundation for language skills.
Discover the benefits and features of our online speech therapy services.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Are Alveolar Sounds in Speech Development?
Alveolar sounds are speech sounds produced by the tongue contacting the alveolar ridge, located just behind the upper front teeth. They are crucial for clear speech and include sounds like /t/, /d/, /s/, /z/, /n/, /l/, and /r/.
2. At What Age Should Children Master Alveolar Sounds?
Children typically master alveolar sounds between the ages of 3 to 6 years. This developmental milestone is important for their overall speech and language proficiency.
3. How Can Parents Help Their Children Develop Alveolar Sounds?
Parents can aid their children’s development of alveolar sounds through articulation therapy, tactile and kinesthetic cues, visual and auditory support, and integrating these sounds into daily activities and reading.
4. Are There Specific Techniques to Teach Each Alveolar Sound?
Yes, each alveolar sound has specific teaching techniques. This includes correct tongue placement, breath control for sounds like /t/ and /d/, and understanding the unique characteristics of each sound, such as the sibilant quality of /s/ and /z/.
5. What Are Some Effective Learning Resources for Alveolar Sounds?
Effective resources include visual articulation cards, auditory repetition exercises, and books rich in alveolar sounds. Select books and activities that emphasize these sounds in a fun and engaging way.
6. How to Identify and Address Challenges in Alveolar Sound Development?
Regular observation and listening to a child’s speech can help identify challenges in alveolar sound development. If challenges are noticed, it may be beneficial to consult a speech therapist for tailored guidance and support.
7. Can Everyday Activities Be Used to Practice Alveolar Sounds?
Absolutely! Integrating alveolar sounds into everyday activities, such as reading, singing, and playful conversation, can reinforce learning and make practice enjoyable for children.
About the Author:
Rajini Darugupally
M.Sc., Speech-Language Pathologist (9+ years of experience)
Rajini is a passionate and dedicated Speech-Language Pathologist with over 9+ years of experience, specializing in both developmental speech and language disorders in children and rehabilitation in adults. Driven by a desire to empower each individual to find their voice, Rajini brings a wealth of experience and a warm, genuine approach to therapy.
Currently, at Wellness Hub, she thrives in a team environment that values innovation, compassion, and achieving results for their clients.
Connect with Rajini to learn more about how she can help you or your loved one find their voice.
Book your Free Consultation Today
Parent/Caregiver Info:
Client’s Details:
* Error Message









